Riparian Zone Definition

Other biomes include savannas tropical rain forests and deserts among many others.
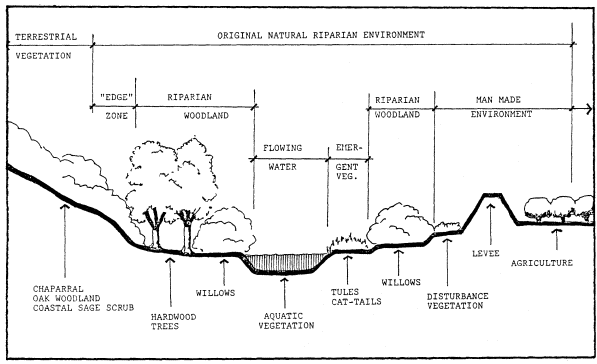
Riparian zone definition. At the edge of a river or relating to. Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the earth. A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream.
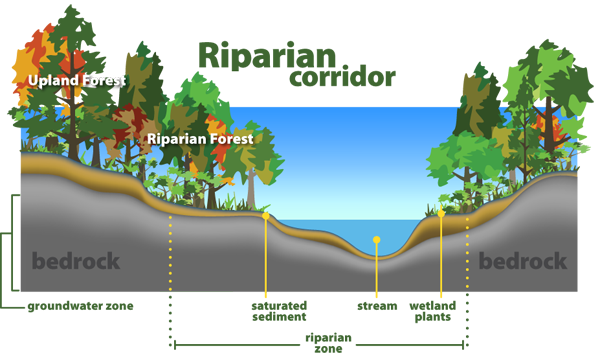
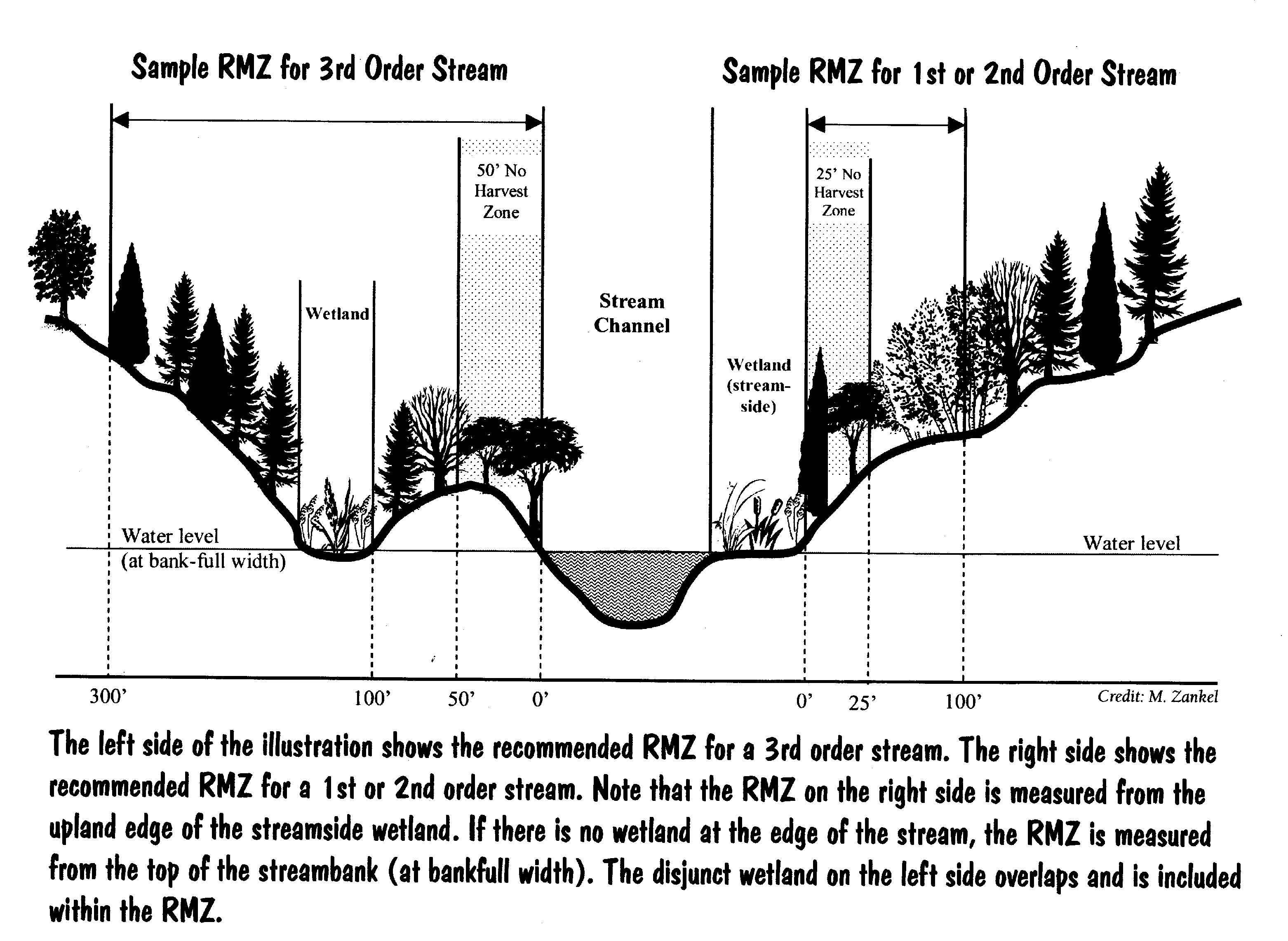
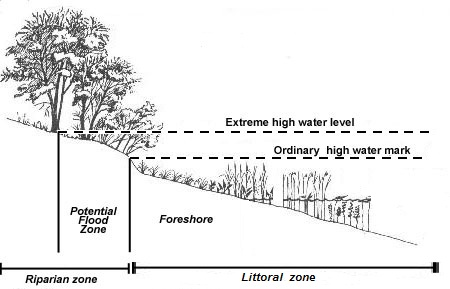
Riparian zone is a transitional area between land and a river or stream. The zones are important in ecology environmental management and civil engineering as they have a critical role in plant biodiversity and soil management among others. The riparian zone is identified as the area immediately adjacent to running fresh water.
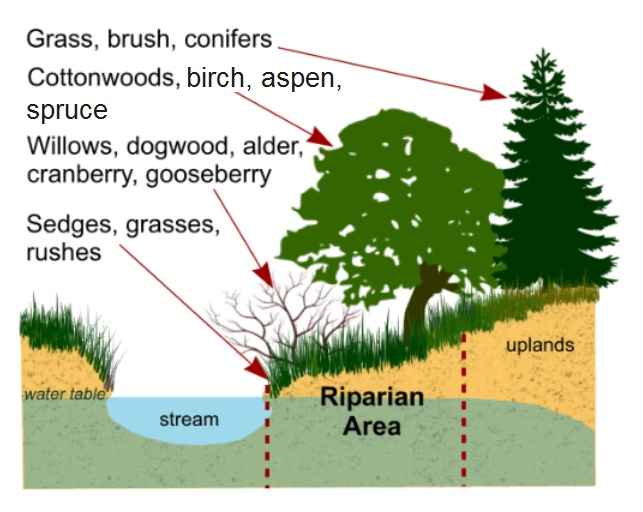
Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks are called riparian vegetation characterized by hydrophilic plants. The riparian zone is one of many different biomes which represent different communities of flora and fauna. Riparian zones include a number of vertebrates that eat fruit and disperse seeds and besides plant propagules semi aquatic mammals are known to inadvertently disperse aquatic invertebrates by carrying them attached to their fur peck 1975.
Riparian zone definition the riparian zone is one of many different biomes which represent different communities of flora and fauna. Riparian zone is also known as riparian buffer zone riparian woodland riparian strip or riparian forest. These areas are unique and diverse and are often the most fertile parts of the landscape.
They include the floodplain as well as the riparian buffers adjacent to the floodplain. The riparian zone is identified as the area immediately adjacent to running fresh water. Riparian zones are the unique environments adjacent to rivers and streams and comprise assemblages of plant and animal communities whose presence can be either directly or indirectly attributed to factors that are stream induced or stream related kauffman and krueger 1984.
In a natural or well managed state riparian areas are important for many reasons. At the edge of a river or relating to this area. Functionally they are three dimensional zones of direct interaction between terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.