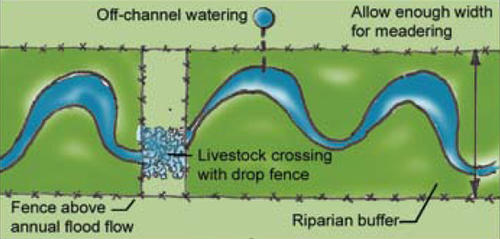
Riparian Buffer Meaning

Through the interaction of their soils hydrology and biotic communities riparian buffers serve many important physical biological and ecological functions klapproth 2009.
Riparian buffer meaning. Translation and definition riparian buffer dictionary english english online. Riparian buffer strips is the technical term that agronomists use to refer to buffer strips on the edge of farm fields. Riparian zone is also known as riparian buffer zone riparian woodland riparian strip or riparian forest.
By definition a riparian buffer is a vegetated buffer strip near a stream which helps to shade and partially protect the stream from the impact of adjacent urban industrial or agricultural land use. It can provide shade a food source and a buffer against pollution from outside sources. A riparian forest bufferis an area adjacent to a stream lake or wetland that contains a combination of trees shrubs and or other perennial plants and is managed differently from the surrounding landscape primarily to provide conservation benefits.
Riparian buffers can also be managed to include trees and shrubs. This technique had long been used in southern europe for agricultural land. 1 riparian buffers are vegetated zones adjacent to streams and wetlands that represent a best manage ment practice bmp for controlling nitrogen entering water bodies.
En wiktionary 2016 noun an area of vegetation around a body of water that gives benefits to the ecosystem in the body of water. Riparian buffers are the lands and assemblages of plants bordering rivers streams bays and other waterways. Riparian zone is a transitional area between land and a river or stream.
Relating to or living or located on the bank of a natural watercourse such as a river or sometimes of a lake or a tidewater riparian trees. Learn how they can be used effectively on an acreage or small farm. A riparian buffer or stream buffer is a vegetated area a buffer strip near a stream usually forested which helps shade and partially protect the stream from the impact of adjacent land uses it plays a key role in increasing water quality in associated streams rivers and lakes thus providing environmental benefits with the decline of many aquatic ecosystems due to agriculture riparian.
The zones are important in ecology environmental management and civil engineering as they have a critical role in plant biodiversity and soil management among others.