Define Riparian Zone

Riparian zones provide many environmental and recreational benefits to streams groundwater and downstream land areas.
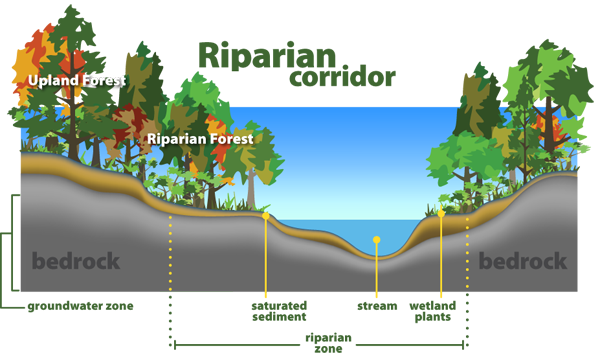
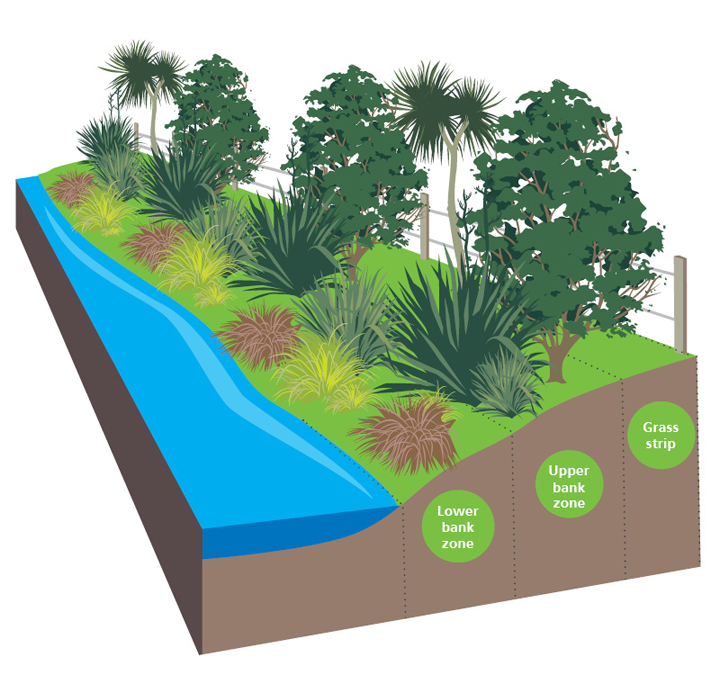
Define riparian zone. A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. Riparian zones are important in ecology environmental resource management and civil engineering because of their role in soil conservation their habitat biodiversity and the influence the. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks are called riparian vegetation characterized by hydrophilic plants.
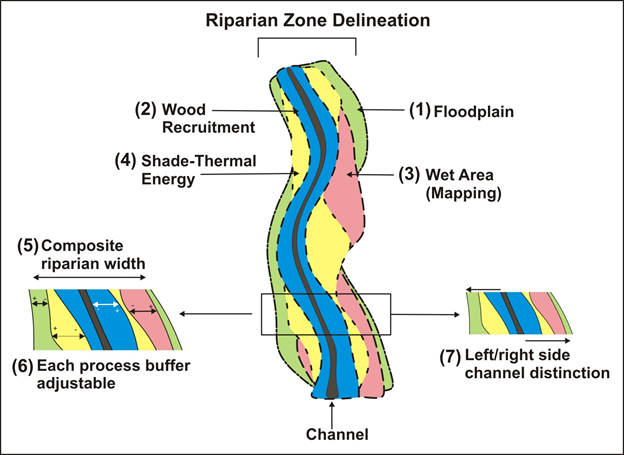
At the edge of a river or relating to this area. Functionally they are three dimensional zones of direct interaction between terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Riparian zone is a transitional area between land and a river or stream.
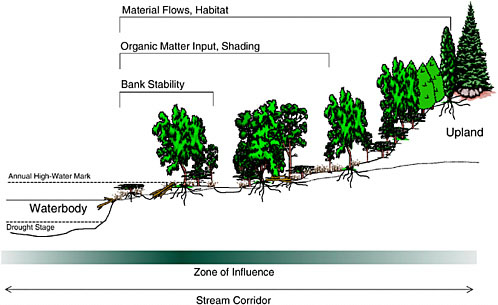
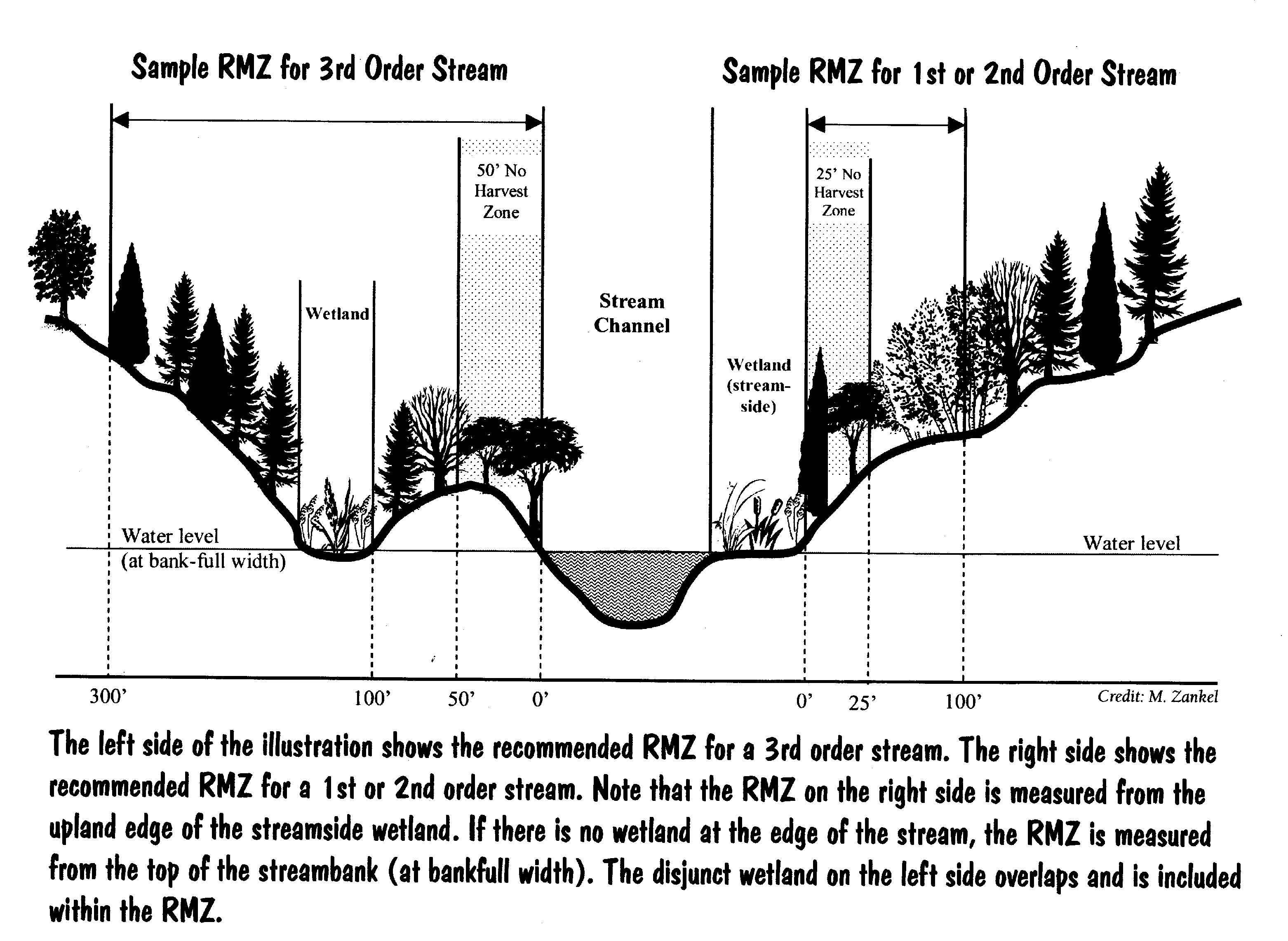
Riparian zones are the unique environments adjacent to rivers and streams and comprise assemblages of plant and animal communities whose presence can be either directly or indirectly attributed to factors that are stream induced or stream related kauffman and krueger 1984. First appearing in english in the 19th century riparian refers to things that exist alongside a river such as riparian wetlands habitats trees etc. They include the floodplain as well as the riparian buffers adjacent to the floodplain.
Riparian zone is also known as riparian buffer zone riparian woodland riparian strip or riparian forest. Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the earth. Riparian zones are the areas bordering rivers and other bodies of surface water.
Some river communities have laws called riparian rights referring to the rights of those owning land along a river to have access to the waterway. The riparian zone is identified as the area immediately adjacent to running fresh water. At the edge of a river or relating to.
Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks are called riparian vegetation characterized by hydrophilic plants. Other biomes include savannas tropical rain forests and deserts among many others. The zones are important in ecology environmental management and civil engineering as they have a critical role in plant biodiversity and soil management among others.