Define Riparian Habitat

Values and functions of riparian areas.
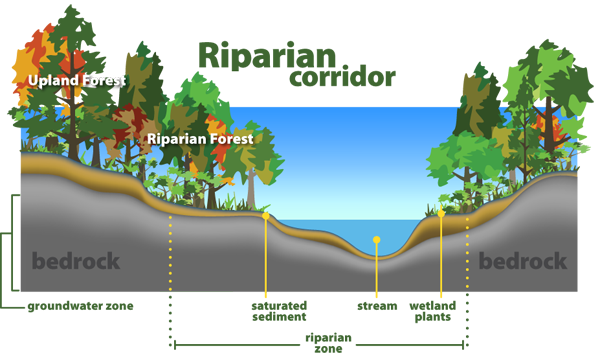
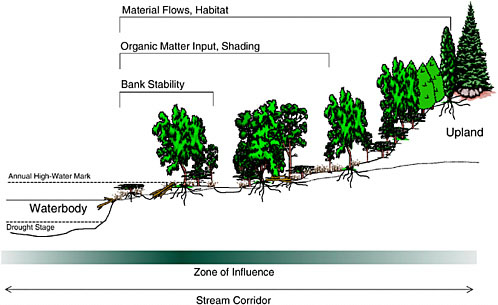
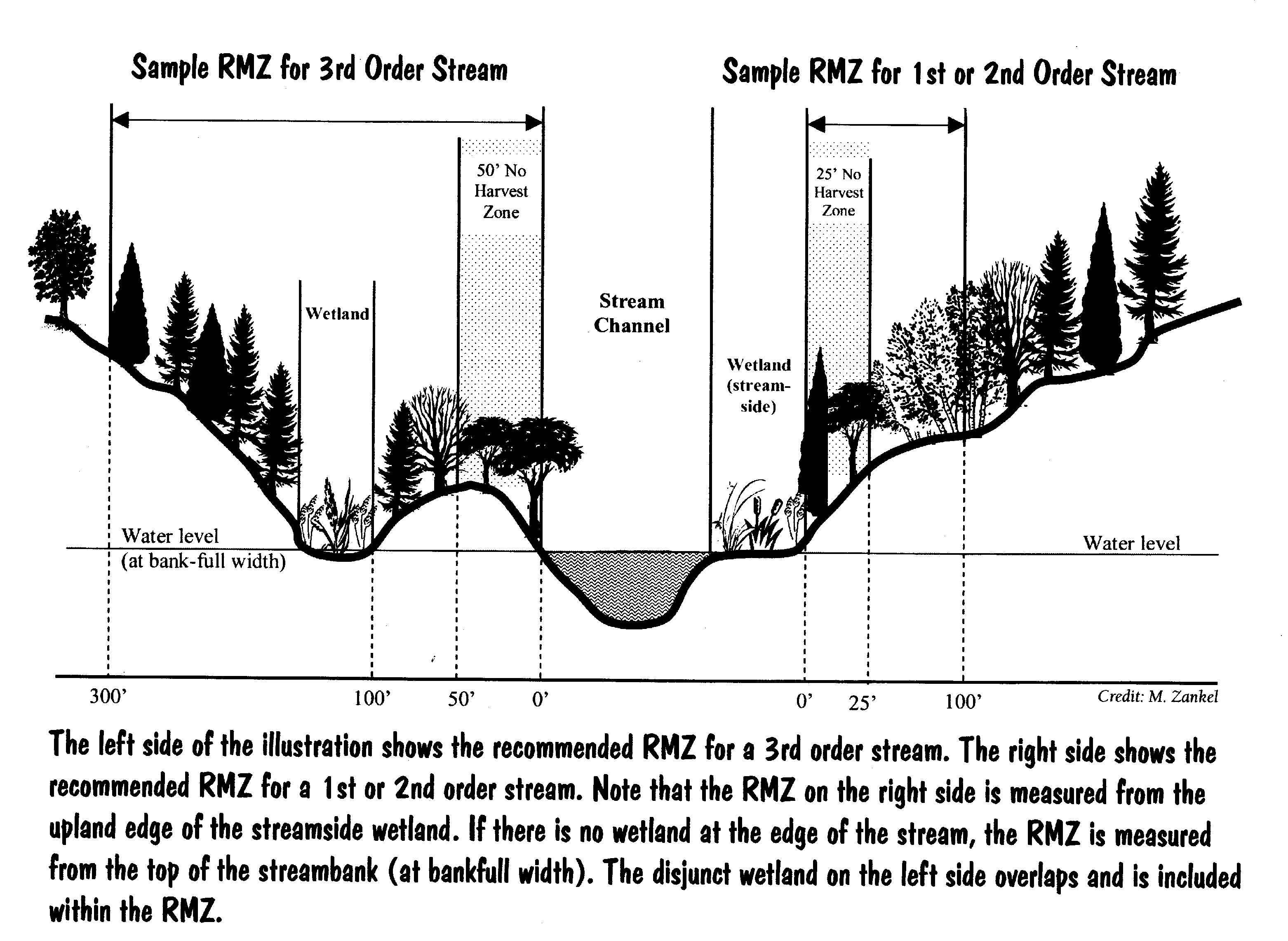
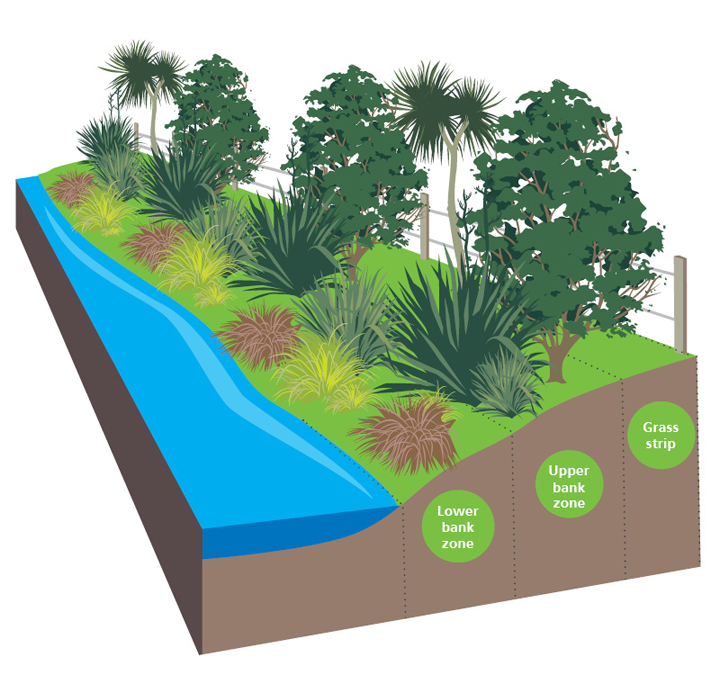
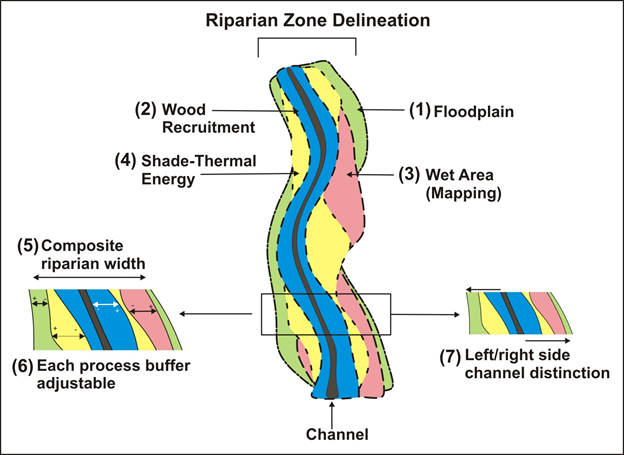
Define riparian habitat. Riparian habitat means land adjacent to water bodies as well as submerged land such as streambeds which can provide functional habitat for salmonids and other fish and wildlife species. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks are called riparian vegetation characterized by hydrophilic plants. Aquatic coarse woody debris or coarse woody habitat cwh coarse woody material coarse woody structure large woody debris can be defined as trees and tree fragments both living and dead that have fallen into lakes streams and rivers from the riparian zone figure 1.
In many areas the separation of the riparian zone from the upland is not distinct. Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the earth. Riparian forests fringe many of the world s unperturbed lentic i e lakes and lotic i e rivers streams systems.
Riparian areas are the major providers of habitat for endangered and threatened species in the western desert areas. A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. Riparian definition is relating to or living or located on the bank of a natural watercourse such as a river or sometimes of a lake or a tidewater.
Definition noun a riparian habitat or riparian zone is a type of wildlife habitat found along the banks of a river stream or other actively moving source of water such as a spring or waterfall. The zones are important in ecology environmental management and civil engineering as they have a critical role in plant biodiversity and soil management among others. In the humid east the riparian areas are more similar to the uplands.